Most technical subjects use a lot of jargon words, with the television, video and film industries using more than their fair share. Thankfully ASPECT RATIO is one of the easier terms to understand, so if you have come across this phrase and wondered what it is all about, this article should help answer your question.
Whilst many of the terms used in the audio-visual industries are extremely technical in nature and can be quite confusing and difficult to understand, aspect ratio thankfully is not one of them. Once you have grasped the concept of aspect ratios you should be able to confidently select the preferred aspect ratio for your video project and understand the reasons why.
Ratios
Before we consider aspect ratios specifically, perhaps a quick recap of what a ratio actually is might be in order, especially for those who struggle to remember their high school mathematics.
A ratio can be defined as:
The numerical relation between two quantities of similar things.
Ratios are convenient ways of comparing relative amounts of something. A simple ratio represents how much there is of one thing (A) to another thing (B).
Ratios are similar to fractions and indeed can be expressed as such amongst other ways:
- A to B
- A : B
- A/B
Like fractions, ratios can also be simplified by finding the highest common factor and dividing each side of the ratio by this factor, e.g. a ratio of 4:8 is identical to the ratio 1:2 (divide both sides of the ratio by the same factor 4).
Aspect Ratios
One of the definitions of the word aspect is:
Appearance to the eye.
It is this definition of the word aspect that we are interested in with our discussion of aspect ratios, as these ratios are concerned with the ratios of visual images, in particular video screens.
The Important Bit
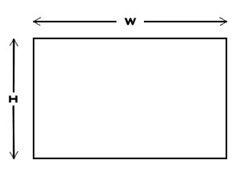 Aspect ratios are the ratio of the width of a screen (or image) in relation to its height and are typical expressed as proper ratios (not fractions) with the width component quoted first.
Aspect ratios are the ratio of the width of a screen (or image) in relation to its height and are typical expressed as proper ratios (not fractions) with the width component quoted first.
For example the aspect ratio of the rectangle to the right is expressed as:
- Width : Height
- W : H
These ratios are usually expressed in words as “width by height”. As such a common example of a 16:9 wide-screen television format would be quoted as “sixteen by nine”.
Size Doesn’t Matter; Really!
Video aspect ratios give no indication as to the size of a screen or image, but are rather an indication of its shape.
For example, if you had a massive screen that was one mile wide and one mile high, it would have an aspect ratio of:
- Width : Height
- 1 mile : 1 mile
- 1 : 1
Such a screen is obviously a square with sides of equal length. If next to this monstrous screen we had another, smaller screen of 10 centimetres wide and 10 centimetres high, this smaller screen would also be square and have an aspect ratio of 1:1.
Quality is Irrelevant to Aspect Ratios
As well as aspect ratios giving no indication as to the size of a screen or image, nor do they give any information about a screen or image’s quality or resolution.
Our small 10cm x 10cm screen in the above example could have one pixel per square centimetre, which would give it a total of 100 pixels. Alternatively it could have one pixel per square millimetre, in which case it would contain 100 pixels in one square centimetre and a total of 10,000 pixels in the whole screen; obviously a far higher resolution and therefore image quality, but still with a 1:1 aspect ratio.
Common Aspect Ratios
TV Aspect Ratios
In the world of domestic television there are two predominant screen aspect ratios commonly in use today; 4:3 and 16:9.
4:3
This aspect ratio, referred to as “4 by 3”, was the standard TV aspect ratio throughout the 20th century. This ratio is slightly off-square with the width of the screen being about 30% wider than its height.
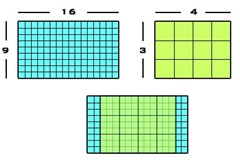
This ratio is sometimes referred to as 12:9, or in a normalised ratio (relative to a height of 1) as 1.33:1.
16:9
This aspect ratio is referred to as “16 by 9” and is the new standard for modern wide-screen and high-definition TV. This ratio is just over 30% wider than the older 4:3 standard as can be seen in the diagram above.
As a normalised ratio this aspect ratio is quoted as 1.78:1.
Cinema Aspect Ratios
While the world of TV is fairly simple regarding its variety of aspect ratios, the cinematic world is somewhat more convoluted. However, there are two cinematic aspect ratios that have become more prevalent.
The most common aspect ratio, used for the majority of US and UK theatrical presentations, is 1.85:1. The other reasonably common standard is 2.35:1, sometimes called Cinemascope.
What is the Best Video Aspect Ratio?
A commonly asked question is “What aspect ratio should I use for my videos?”
Firstly, there is no such thing as a “best” aspect ratio as the choice of aspect ratio is governed by many factors. The answer depends on your circumstances, such as the equipment you have available to record and edit videos on, and perhaps more importantly, where your videos are most likely to be played and on what equipment.
Wide-screen or Standard?
Thankfully in the world of consumer video equipment the available choices are fairly restricted; usually either 4:3 or 16:9.
Generally, the best video aspect ratio to use would be the wide-screen 16:9 format. This has undoubtedly become the modern standard and should be your aspect ratio of choice, unless you have compelling reasons to choose otherwise.
Sharing your Videos On-line
If you intend to upload videos on-line to share with others using services such as YouTube then this is even more reason to choose the 16:9 format.
YouTube uses 16:9 aspect ratio players as standard and any other aspect ratio video uploaded will be converted to fit the 16:9 aspect ratio with appropriate black padding bars added to fill the spaces as either pillar boxes or letter boxes.

Great article! I have been using the 16:9 for years now and my parents just now broke down and got a Widescreen TV. I wish I could have shown them this article before they wore me out TV shopping.